Introduction to Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is a widely used approach in Forex trading, where traders analyze historical price data and chart patterns to forecast future price movements. Unlike fundamental analysis, which focuses on economic and political factors, technical analysis relies on the premise that past price movements can provide valuable insights into future price trends.
By using a variety of charting tools and technical indicators, traders can make informed decisions about when to enter or exit a trade. At platforms like PFD Markets, traders can access a range of charting tools to support their technical analysis, enhancing their ability to make well-researched trading decisions.
Key Concepts in Technical Analysis
Technical analysis involves analyzing price movements through charts and indicators. Traders use various tools to identify trends, reversals, and potential entry or exit points. Some of the fundamental concepts in technical analysis include:
- Price Action: The movement of prices over time. It forms the foundation for all chart patterns and indicators.
- Trends: Trends are the direction in which the price of an asset is moving. Traders seek to trade with the trend, buying in uptrends and selling in downtrends.
- Support and Resistance Levels: These are key price levels where the market has historically reversed direction. Support is a price level where demand is strong enough to prevent further declines, while resistance is where selling pressure tends to push the price back down.
- Momentum Indicators: Tools used to measure the strength of a price movement, such as Relative Strength Index (RSI) and Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD).
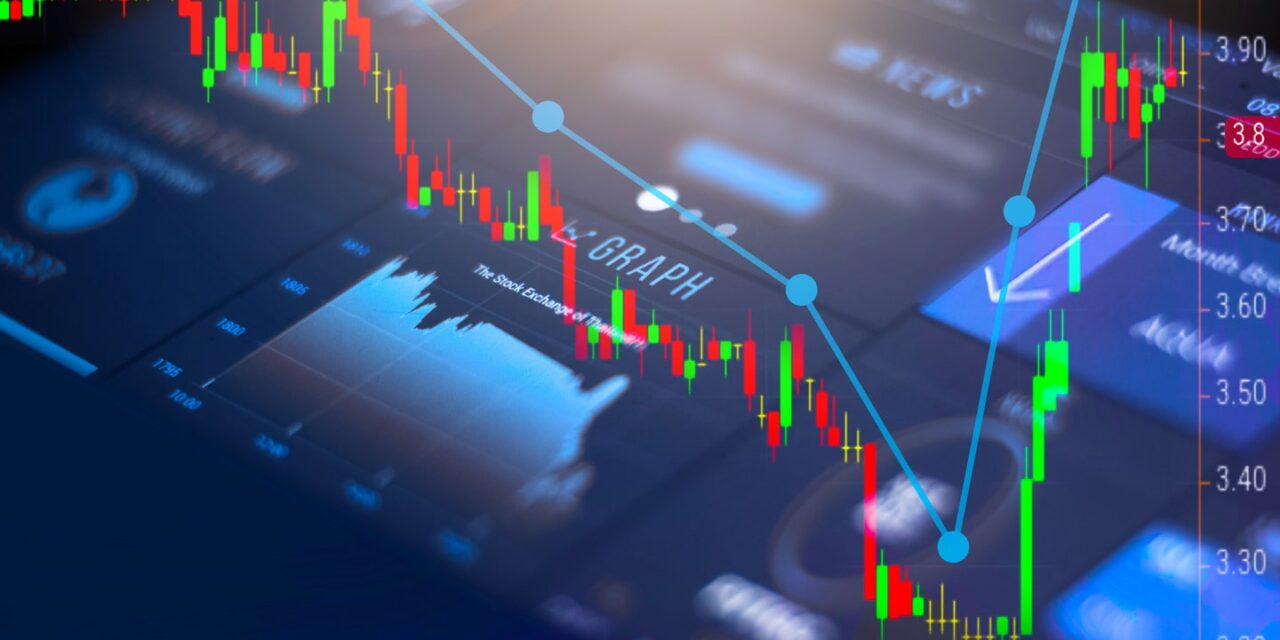
Types of Charts in Technical Analysis
Charts are a key component of technical analysis. They visually represent price movements over time and allow traders to spot patterns and trends that may indicate future price movements. There are several types of charts commonly used in technical analysis:
1. Line Charts
Line charts are the simplest form of chart used in technical analysis. They plot a single line based on the closing prices of an asset over a specific period. This type of chart is helpful for identifying general trends, but it does not show as much detail as other chart types, such as bar or candlestick charts. Line charts are most commonly used for identifying long-term trends.
2. Bar Charts
Bar charts display more information than line charts. Each bar on a bar chart represents the price movement for a specific time period, such as a minute, hour, or day. The vertical line represents the range between the highest and lowest prices during that period, while the horizontal lines on the left and right show the opening and closing prices, respectively. Bar charts are useful for analyzing price action and determining the market’s direction.
3. Candlestick Charts
Candlestick charts are one of the most popular chart types in technical analysis. Each candlestick represents the price movement during a specific time period and consists of a body and wicks (or shadows). The body shows the opening and closing prices, while the wicks represent the highest and lowest prices during that period. Candlestick charts provide more information than bar charts, and patterns formed by candlesticks can be used to predict future price movements.
Candlestick patterns such as “Doji,” “Engulfing,” and “Hammer” are commonly used to identify potential reversal points in the market.
Key Technical Indicators
In addition to chart patterns, traders use a variety of technical indicators to analyze price action and identify potential entry and exit points. Some of the most commonly used technical indicators in Forex trading include:
1. Moving Averages (MA)
Moving averages are one of the most widely used indicators in technical analysis. They smooth out price data to create a trend-following indicator that helps traders identify the direction of the market. There are two main types of moving averages:
- SMA (Simple Moving Average): The SMA is calculated by averaging the closing prices of an asset over a specific number of periods.
- EMA (Exponential Moving Average): The EMA gives more weight to the most recent prices, making it more responsive to price changes.
Moving averages are often used to identify the overall trend. For example, if the price is above a moving average, the market is considered to be in an uptrend. Conversely, if the price is below a moving average, it suggests a downtrend.
2. Relative Strength Index (RSI)
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a momentum oscillator that measures the speed and change of price movements. RSI values range from 0 to 100 and are typically used to identify overbought or oversold conditions in the market. An RSI above 70 indicates that an asset is overbought, while an RSI below 30 suggests that it is oversold. RSI can also be used to identify potential trend reversals.
3. Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
The MACD is a trend-following momentum indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages of an asset’s price. The MACD line is calculated by subtracting the 26-period EMA from the 12-period EMA. The MACD is typically used to identify potential buy and sell signals by analyzing crossovers between the MACD line and the signal line.
4. Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands consist of a simple moving average (SMA) and two standard deviation lines, which are plotted above and below the SMA. The bands widen or narrow based on market volatility. When the price reaches the upper band, the asset may be overbought, while the lower band suggests oversold conditions. Bollinger Bands are commonly used to identify periods of high or low volatility.
Combining Technical and Fundamental Analysis
While technical analysis is a powerful tool on its own, many successful traders choose to combine it with fundamental analysis to get a more comprehensive view of the market. Fundamental analysis focuses on the economic factors that influence currency prices, such as GDP, interest rates, inflation, and geopolitical events. By combining both technical and fundamental analysis, traders can make better-informed decisions that take into account both market trends and underlying economic conditions.
For example, a trader may use technical indicators to identify an overbought or oversold condition in a currency pair. However, before entering a trade, they might check the economic calendar to see if there are any upcoming events (such as a central bank interest rate decision) that could affect the currency’s value. This approach can help traders avoid potential market shocks and improve their risk management strategies.
Conclusion
Technical analysis is a vital tool for traders in the Forex market. By analyzing historical price data, chart patterns, and technical indicators, traders can make informed decisions and improve their chances of success. Whether you are using line charts, bar charts, or candlestick charts, the key to effective technical analysis is understanding how to interpret market trends and signals.
At platforms like PFD Markets, you can access a wide range of charting tools and technical indicators to enhance your trading strategies. While no single chart type or technical indicator is universally superior, combining technical and fundamental analysis can provide a more comprehensive view of the market, helping you make smarter, more informed trading decisions.